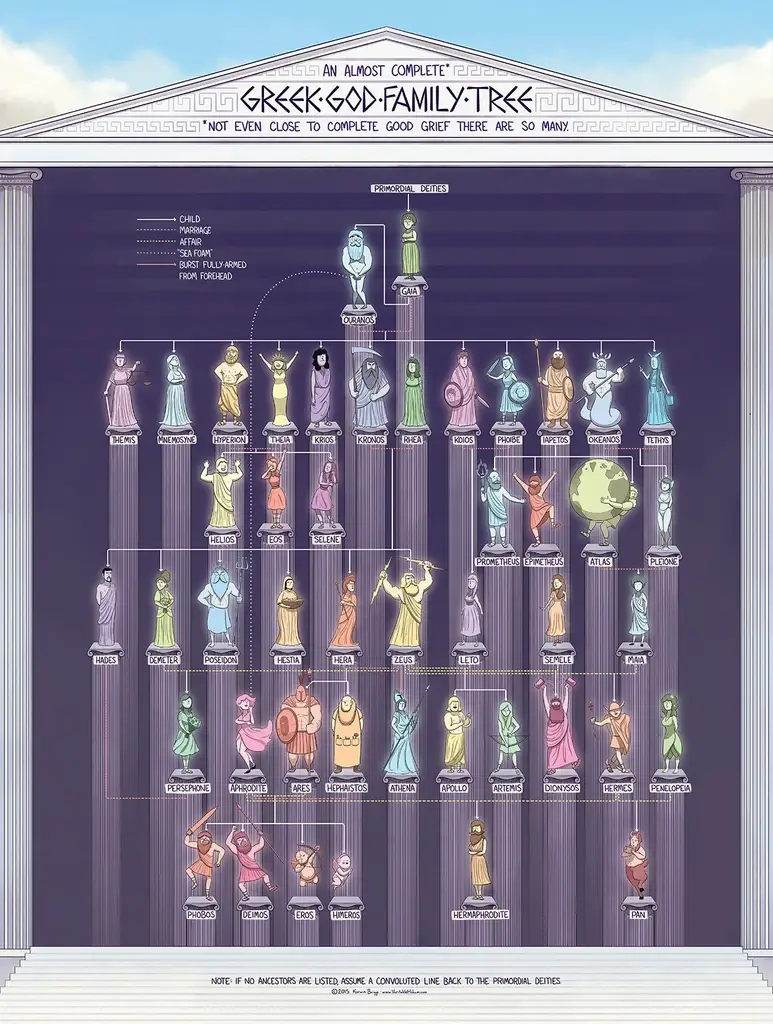
The family tree of the Greek Gods is an elaborate and detailed web of kin connections. Zeus, the powerful King of the gods, topped the pantheon of Greek deities. He had Hera, the Queen of the gods, as his wife. The couple was blessed with three offspring: Ares, the god of war; Athena, the goddess of wisdom; and Apollo, the god of the sun.
Zeus and Hera also had other children, some of whom were renowned for the mischief they caused on Olympus. These included the mischievous Hermes, god of thieves; Dionysus, god of wine; and Eris, goddess of discord. Zeus also had a number of illegitimate children who often clashed with their siblings to gain power and influence. These included Tyche, goddess of luck; Nemesis, goddess of divine retribution; and Aphrodite, goddess of love.
Hera’s great rival was Demeter, goddess of the harvest. She had a daughter named Persephone who was stolen away by Hades, god of the underworld. Other gods connected with the underworld included Hecate, goddess of witchcraft; Charon, ferryman of the dead; and Thanatos, god of death.
Many other gods and goddesses were part of the Greek pantheon. These include Hephaestus, god of fire; Poseidon, god of the sea; Artemis, goddess of the hunt; and Hermes, god of travelers. The sea-dwelling Nereids were also important figures in Greek mythology.
The extensive family tree of the gods was further complicated by the addition of deities from other cultures. The Egyptian goddess Isis had a relationship with Osiris that resulted in an offspring named Horus; Dionysus had two sons, Priapus and Zagreus; and the Minoan goddess Rhea gave birth to Zeus’s daughter, Persephone.
The intricate relationships between gods, goddesses, and mortals were often depicted in art and literature throughout ancient Greece. This can be seen in works such as Homer’s Iliad and Odyssey, Hesiod’s Theogony, and Ovid’s Metamorphoses. These works helped to further illustrate the complex dynamics of the Greek Gods family tree.
The pantheon of gods in Greek mythology is a fascinating subject that continues to captivate people today. Through exploring this intricate family tree, we can gain a greater understanding of the gods and goddesses who populated ancient Greece.
Related: Encanto family tree (Madrigal Family), Hades family tree, Aphrodite family tree
What is the Greek Gods family tree?
The Greek Gods family tree is a complex and intricate network of familial relationships between gods, goddesses, and mortals. At the head of the pantheon was Zeus, King of the gods. He was married to Hera and together they had three children. Zeus also had a number of illegitimate children who often clashed with their siblings to gain power and influence.
Who are some of the gods in the Greek pantheon?
Some of the gods in the Greek pantheon include Ares, god of war; Athena, goddess of wisdom; Apollo, god of the sun; Hermes, god of thieves; Dionysus, god of wine; Eris, goddess of discord; Tyche, goddess of luck; Demeter, goddess of the harvest; Poseidon, god of the sea; Artemis, goddess of the hunt; Hephaestus, god of fire; and Hecate, goddess of witchcraft.
What works of literature depict the Greek Gods family tree?
Some famous works of literature that depict the Greek Gods family tree include Homer’s Iliad and Odyssey, Hesiod’s Theogony, and Ovid’s Metamorphoses. These works helped to further illustrate the complex dynamics between gods, goddesses, and mortals in Ancient Greece.
What is the significance of exploring the Greek Gods family tree?
By exploring the intricate relationships between gods, goddesses, and mortals in the Greek Gods family tree, we can gain a greater understanding of this captivating subject from ancient Greece. This helps us to appreciate how gods and goddesses were represented in art and literature, as well as how they interacted with each other and mortals.
Who were the siblings of Zeus?
The siblings of Zeus included Poseidon, god of the sea; Hades, god of the underworld; Demeter, goddess of the harvest; and Hestia, goddess of hearth and home. Zeus also had a number of illegitimate children who often clashed wiith their siblings to gain power and influence.
What gods were associated with the underworld?
Gods associated with the underworld included Hades, ruler of the dead; Hecate, goddess of witchcraft; Charon, ferryman of the dead; and Thanatos, god of death. Other deities often connected with the underworld in Greek mythology include Nyx (goddess of night) and Erebus (god of darkness).
What was the relationship between Isis and Osiris?
The relationship between Isis and Osiris was one of love. They had an offspring named Horus who was born after Osiris’s death. Isis then resurrected her husband from death through her magical powers. She was a devoted wife and mother, often seen as the ideal of female devotion.
What gods were associated with war?
Gods associated with war in Greek mythology include Ares, god of war; Athena, goddess of wisdom; Hephaestus, god of fire; Zeus, king of the gods; Apollo, god of the sun; and Hermes, messenger of the gods. Each had their own particular domain when it came to warfare and strategy.
Who were the siblings of Demeter?
The siblings of Demeter included Zeus (father); Poseidon, god of the sea; Hades, ruler of the underworld; Hestia, goddess of hearth and home; and Hercules, hero of many Greek myths. Demeter was also the mother of Persephone, who she shared with her brother Zeus.
Related: Hercules family tree
Who were the children of Aphrodite?
The children of Aphrodite include Eros, god of love; Anteros, god of mutual love; Deimos and Phobos, gods of fear and terror; Harmonia, goddess of harmony; and Hathor (also known as Ishtar), goddess of fertility. Other offspring attributed to Aphrodite include Priapus, god of fertility; Hermaphroditus, a combined male-female figure with special powers; Tyche (Fortuna), goddess of luck; and Peitho, goddess of persuasion.
What were the roles of Athena and Apollo?
Athena was the goddess of wisdom, courage, justice, and strategic warfare while Apollo was the god of music, archery, prophecy, healing, poetry, and the sun. Both deities had a strong presence in Greek mythology and featured prominently in many tales. They were also both associated with arts and culture as well as military might.
FAQ:
Q: What is Greek Gods family tree?
A: Greek Gods family tree is a visual representation of the relationships between the gods and goddesses in Greek mythology. It shows the genealogy of the main characters, their birthplace, and their significance.
Q: Who are the Olympian gods?
A: The Olympian gods are the twelve main gods and goddesses who lived on Mount Olympus. They were the most powerful and important gods in the Ancient Greek pantheon.
Q: Who are Hermes and what is his role in Greek mythology?
A: Hermes is the messenger of the gods and the god of commerce, trade, and thieves. He is also associated with good luck, fertility, and athletic competitions.
Q: Who is Hera and what is her role in Greek mythology?
A: Hera is the queen of the gods and the goddess of marriage, fertility, and childbirth. She is also the goddess of the sky and the wife of Zeus, the king of the gods.
Q: Who is Poseidon and what is his role in Greek mythology?
A: Poseidon is the god of the sea, earthquakes, and horses. He is one of the twelve Olympian gods and is often depicted with a trident, which he used to create or destroy things in the sea.
Q: Who is Dionysus and what is his role in Greek mythology?
A: Dionysus is the god of wine, parties, and fertility. He is often depicted as a young man with a grapevine wreath on his head and a drinking cup in his hand.
Q: Who is Artemis and what is her role in Greek mythology?
A: Artemis is the goddess of the hunt, the wilderness, childbirth, and virginity. She is also the protector of young women and is often depicted with a bow and arrows.
Q: Who is Ares and what is his role in Greek mythology?
A: Ares is the god of war, violence, and bloodshed. He is often depicted as a tall muscular man with a spear or sword.
Q: What is Greek mythology?
A: Greek mythology is a collection of stories and legends about gods, heroes, and creatures from Ancient Greece. These stories were used to explain natural phenomena, religious beliefs, and human behavior.
Q: Who are the goddesses in Greek mythology?
A: The goddesses are the female deities in Greek mythology. They are powerful and influential figures who have control over various aspects of life such as love, war, wisdom, and childbirth.
Q: Who are Cronus and Uranus in Greek mythology?
A: Cronus is the god of time and the leader of the Titans. Uranus is the god of the sky and the father of the Titans. Both of these gods play important roles in the creation myth of the Ancient Greeks.

Elizabeth Miller is a seasoned family tree researcher with over 16 years of expertise in tracing the genealogies of historical, celebrity, and well-known individuals. Holding relevant qualifications, they actively contribute to genealogy communities and have authored articles for prominent publications, establishing their authority in the field. Elizabeth Miller is dedicated to unraveling the intricate family histories of notable figures, helping clients discover their historical roots. Satisfied clients attest to their trustworthiness and the enriching experience of working with them. As a dedicated storyteller who brings history to life through genealogy, Elizabeth Miller is a reliable and authoritative source for those seeking to explore the family trees of historical, celebrity, and well-known personalities.